This is the latest installment of BACKED’s Future of Finance investment research. The last article published in September focussed on blockchain technology in the age of AI. Today we explore the advances in financial infrastructure in an article by Alex Brunicki, co-founding partner of BACKED.
In the blockchain sector where product market fit has been tough to establish , stablecoins have now emerged as a notable success story. This was underscored by Stripe’s recent acquisition of Bridge, a stablecoin infrastructure provider, for $1.1 billion. Bridge processed over $1 trillion in payment volumes in 2023, helping businesses accept stablecoin payments without having to directly deal in digital tokens. As stablecoins continue to gain traction, we believe they have the capability to reshape the landscape of global finance.
What are Stablecoins?
Read on for those in the know. Stablecoins provide a stable, swift, digital currency for payments, remittances and trading in crypto markets for B2B and B2C. Stablecoins – as their name suggests – address a key pain point of the volatility typical of cryptocurrencies. This also helps in emerging markets where inflation and changes in currency valuations are rife. Thus stablecoins allow for cross-border transactions, bypassing traditional banking infra, and near-instant settlements.
Stablecoins offer a multi-faceted, compelling value proposition to a diverse set of users. In nations that experience high inflation and currency devaluation, stablecoins can serve as a self-sovereign, anti-inflation hedge. For developed nations, stablecoins provide an alternative to traditional money movement rails, offering lower costs, instant settlement and global access, all on a single, transparent ledger.
The Rise of Stablecoins
The growth of stablecoins has been remarkable. As of December 2024, the total supply of stablecoins reached approximately $192.68 billion, reflecting a 129.76% CAGR from January 2019. Adjusted stablecoin volumes and transaction count (after excluding high-frequency trading and bots) have also grown consistently, with volumes of $670.66b and transaction counts of 123.59m as of November 2024, representing a 248.25% and 239.54% CAGR respectively. Stablecoin use in speculative trading, measured by ratio of daily trading volume to circulation, has also declined 90% over the past five years from 5.25 to 0.51. In other words, every dollar of stablecoin only supports about $0.51 of daily trading volume in 2023, as compared to $5.25 back in 2019.
In the following sections, we first share our mental model when assessing companies that are dealing with stablecoins before attempting to map the existing landscape and finally ending with areas that are of interest to our Future of Finance investment thesis.
Our Mental Model
Our mental model focuses on two key defining areas which we think provide insights into a company’s potential for success and scalability in this rapidly growing sector: target geographies and team expertise.
- The first consideration is the company’s target geographies.
Their choice of geographical location directly influences market sizing, customer segmentation, regulatory environment and the corresponding compliance requirements. We view geographies as two broad buckets: countries with a stable currency and countries with a highly inflationary currency. The former can use stablecoins as a form of cheaper, faster way to move money globally, while the latter can use stablecoins as a self-sovereign medium of exchange. In view of their geographical selection, we then look at how companies design their business models, go to market strategies and customer acquisition strategies. We also closely examine the regulatory environment in their chosen markets, as the regulatory framework for stablecoins varies widely across jurisdictions and can greatly affect a company’s operational feasibility and growth prospects. - The second Another important consideration is the relevant expertise of the team.We are looking for teams with skills that span across DeFi, CeFi, regulation and also banking. A strong understanding of regulatory regimes and compliance practices is a must, alongside deep local expertise which is crucial for customer acquisition. The name of the game is total payment volumes processed, so we focus intently on, and any traits which will drive that.
Mapping the Existing Landscape
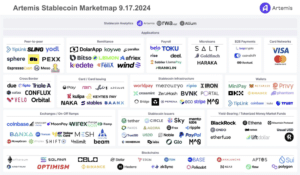
SOURCE: Artemis Stablecoins Landscape
Before we dive into the areas where we are spending most of our time, we felt that it was important to share a quick overview of the stablecoins landscape. We broke them down into two distinct categories: Infrastructure and Applications:
INFRASTRUCTURE
Payment orchestration layer
Companies in this sub-vertical provide low level orchestration APIs that abstract the stablecoin layer away from the fiat layer. This enables users to interact and use stablecoins without having to handle the exchange, transfer and settlement elements of the transaction. The beauty of this abstraction layer means that companies that deal with payments can go global on day 1 without huge capital investment to set up balances in the countries they work in.
Notable Companies: Bridge, Iron.xyz, BVNK, Fractal Payments
Blockchain settlement layer
Companies in this sub-vertical provide the transparent, immutable and unified ledger to settle money movements via stablecoins. Money movement settlements are notoriously difficult and expensive to maintain, which blockchains seek to address.
Notable Companies: Ethereum, Solana, Stellar, Ripple
Stablecoin Issuers
Companies in this sub-vertical issue and manage their stablecoins in circulation. The most widely used stablecoins are fiat-based, and these companies handle the link between the fiat and stablecoin layer. While there are also decentralised stablecoins, they do not provide a bridge to the fiat system and hence are heavily skewed towards native blockchain economies.
Notable Companies: Circle, Tether, Paxos
Stablecoin Custodians
Companies in this sub-vertical safeguard and manage assets that back the stablecoins issued. They are high on compliance and adhere to regulatory requirements. They sometimes offer adjacent services like treasury management.
Notable Companies: Anchorage, Fireblocks
Wallets
Companies in this sub-vertical provide the front-facing user interface to hold, send and receive stablecoins. These are usually more prominent for B2C businesses as the end user has self-custody of their assets and use the wallet to perform transactions. In the case of B2B businesses, these wallets are usually abstracted to feel more like traditional bank accounts.
Notable Companies: Metamask, Coinbase Wallet, Phantom Wallet
Last Mile Infrastructure
Companies in this sub-vertical facilitate the transfers between stablecoins and fiat. Also known as on & off ramps, they are highly critical end points to bridge the traditional financial system and the on-chain financial system.
Notable Companies: Coinbase, Onramper, Transak
APPLICATIONS
P2P Payments
These companies typically facilitate C2C transactions, with rates set independently between the buyers and sellers. The user interface may also sometimes be abstracted, with examples such as Minipay (built within Opera) and Tiplink (send and receive stablecoins with just a google log in).
Notable Companies: Minipay, Tiplink, Sling, Sphere
Payroll
These companies enable businesses to pay employees and contractors in stablecoins, offering solutions for global workforce management, compliance, and cross-border salary disbursements.
Notable Companies: Request Finance, Toku, LlamaPay
Micro Loans
These companies use stablecoins to provide small, short-term loans to individuals or small businesses, often in areas with limited banking services.
Notable Companies: Goldfinch, Haraka
Cross Border Payments
These companies receive and send transactions globally via stablecoin rails, reducing costs and settlement times significantly.
Notable Companies: Fractal Payments, Lemon, Bitso, Felix
Our Focus Areas
Money Movement Infrastructure
The Opportunity
Cross border money movement involves a few major components: messaging networks, correspondent banking networks, payment processing systems and central banks.
Let’s break it down with an example of moving funds between the US to the UK.
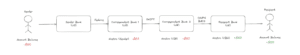
Say we are in the US and we want to send $100 to the UK:
- We instruct our Sender Bank (US) that we want to send $100 to the UK
- The bank runs the necessary KYC / AML / compliance checks
- They debit the sender’s account by $100
- Sender Bank (US) sends a message to Correspondent Bank (US) about the $100 payment to the recipient in the UK
- The message is sent domestically via Fedwire
- The Nostro Account of the Sender Bank (US), which is an account held at Correspondent Bank (US), is debited $100
- Correspondent Bank (US) then sends a message to Correspondent Bank (UK) about the $100 payment to the recipient in the UK
- The message is sent internationally via SWIFT
- The Nostro Account of Correspondent Bank (US), which is an account held at Correspondent Bank (UK), is debited $100
- Correspondent Bank (UK) then sends a message to Recipient Bank (UK) about the $100 payment to the recipient in the UK
- The message is sent domestically via ACH / BACS
- The Nostro Account of Recipient Bank (UK), which is an account held at Correspondent Bank (UK), is credited $100
- The Recipient Bank (UK) credits the recipient with $100
- There may be FX involved if the recipient receives the funds in GBP
Every bank in between will have their own internal compliance process and fees to process the funds, which result in long processing times and expensive transfers. Banking hours also play a role in terms of how fast funds can be processed across borders. There is also the need to rebalance all the nostro and vostro accounts across all banks, which involves settlement from payment processing systems and central banks. All in all, you can see why cross border payments take such a long time.
Blockchains and by extension stablecoins, can solve the complex web of correspondent banking, specifically the nostro / vostro accounts settlement since blockchains operate on a single, open ledger. Stablecoins give pseudo-anonymity and a standard to move funds anywhere globally, but the entry and exit point allows authorities to retain KYC / AML best practices before the funds move back into their economy.
Our Evaluation
Cross border payment solutions have a vanilla business model where they take a fee from the total payments volume processed. We are interested in companies building the infrastructure to enable cross border money movements, and also the applications serving and delivering the requests for the end users.
Infrastructure
Companies on the infrastructure side will look similar to Bridge, which involves a tech stack that is flexible and nimble to cater to the users’ needs. Such businesses will take a launch and expand growth strategy, such as gaining a foothold in a specific geography, saturating it before expanding into other geographies. The business can also expand through introducing new product offerings, such as a localised front end application, treasury management services, remittance offerings, payroll execution and tracking etc.
The team profile we think are best suited for success is:
- strong technically – to be flexible on their tech stack to work towards the needs of the user
- compliance competent – to ensure they are regulatory compliant to onboard larger B2B clients, and cover more geographies to increase their TAM
Applications
Companies working on the application side will look something like Felix, abstracting the wallet layer, allowing end users to store, send, receive and spend funds in stablecoins. The goal is to become the de-facto stablecoin wallet for a local jurisdiction, and expand on offerings for the end user. Such offerings include money markets, credit cards, bill payments etc.
The team profile we think are best suited for success is:
- Local market expertise – to acquire local customers with unique user habits
- Business development savvy – to expand business offerings to build a moat over their application
Last Mile Infrastructure
The Opportunity
On / Off ramps are a crucial component for stablecoin infrastructure, serving as the gateway between fiat and crypto. The key to building a fiat onramp is integrating with the local banking system and the most efficient way is to go to a Banking as a Service provider who can match the company with a bank. This can then enable the company to open white-labeled accounts for their end users directly through their app’s platform as long as the crypto transactions are legitimate. With stablecoins to go global, on / off ramps are required in various geographies such that money can move seamlessly.
Our Evaluation
The business model is also a fee on the total volumes processed. While it is a cog as part of the bigger stablecoin infrastructure, we are interested in companies that also wrap several end-user features on top of the on / off ramping capabilities. This means building a front-facing app that offers various products for the end user, such as remittance, money market funds, credit cards and any other localised services. Other companies can take the form of B2B, providing a single access point to offer on / off ramp services across multiple geographies where they have the required licenses.
The team profile we think are best suited for success is:
- Regulatory and compliance competent – handling crypto dollars into fiat is a highly regulated / licensed product which serves as a barrier to entry and hence a short term moat. Given the different requirements around money transmitter licensing in various jurisdictions, a team will need the regulatory and compliance know how to secure them
- Strong product focus – owning the end user means building products for the end user and this will be a non-negotiable trait.
EU / UK Stablecoin Issuers
The Opportunity
Investing in a stablecoin issuer in Europe and the UK presents a compelling opportunity due to the growing demand for regulated digital assets and the evolving regulatory landscape. The EU’s Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA), effective from June 30, 2024, and the UK’s proposed regulatory framework create a legal platform for stablecoin businesses, potentially giving these regions an edge in this emerging technology. Additionally, the UK’s proposal to allow stablecoin issuers access to central bank reserves could provide a competitive advantage over the EU, potentially supporting the diffusion of stablecoins for everyday payments.
Our Evaluation
Stablecoins issuers are highly lucrative businesses; they keep custody of the underlying fiat backing the stablecoins and earn a yield on those reserves. For example, Coinbase generates over $150 million quarterly from USDC interest income, representing a lucrative revenue stream that accounts for nearly 25% of the company’s net revenue by simply holding and managing stablecoin reserves.
The team profile we think are best suited for success is:
- Regulatory and compliance competent – team requires deep knowledge of cryptocurrency regulations and strong compliance capabilities are essential to navigate the KYC and AML procedures needed to comply with the complex regulatory requirements
- Robust risk management – essential for stablecoin issuers given it deals with consumer protection, and there are assessment required to maintain their ability to meet redemption requests even during periods of stress
OUR CONCLUSION
In conclusion, at BACKED we firmly believe that stablecoins will form a critical part of the global financial infrastructure in the near future. While we’ve highlighted three key areas of focus in Money Movement Infrastructure, Last Mile Infrastructure, and specifically EU/UK Stablecoin Issuers, we remain open to innovative ideas that can further integrate stablecoins into the global economy.
Our thesis is clear: stablecoins have the potential to revolutionize financial systems worldwide. If this vision aligns with your work, we encourage you to reach out. We are also keen to engage with companies that are actively involved in shaping stablecoin regulation in the UK.
Follow our LinkedIn for latest investments and the next thesis.

